👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 6:05:19 AM
Price-to-Book (P/B)
What is P/B Ratio?
P/B ratio stands for the price-to-book ratio. It is a popular indicator preferred by investors to evaluate a company. When company the P/B ratio between similar companies, a higher P/B ratio generally means that the company is overvalued, and a lower P/B ratio means that the company is undervalued.
Calculation
Book Value is a financial measurement of a company’s net worth (asset (everything the company has the control right of) - liability (properties that the company owes) = what the company owns). It is often used interchangeably with the equity value. By comparing the share price with the book value per share, this handy P/B ratio provides investors with a glimpse of whether the market price (share price) overvalues the company.
- Price-to-Book = Share Price ÷ Book Value Per Share
- Price-to-Book = Market Capitalization ÷ Book Value
- BookValuePerShare = Asset-Liability ÷ Shares Outstanding
How to Use It?
Similar to the P/E ratio, EV/EBITDA, and many other valuation ratios, P/B only becomes useful when comparing similar companies. This is why P/B is called a relative valuation metric. One useful application of the P/B ratio is to compare companies that are in the same industry. Another application of P/B can be compared with the historical P/B ratio, and see how the valuation changes through time.
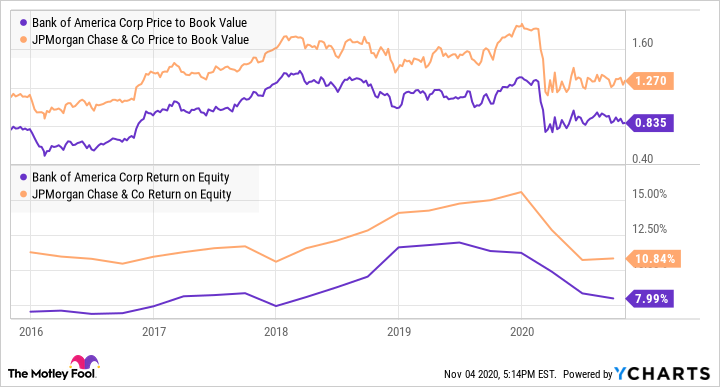
Here is a chart comparing Bank of America Corp’s P/B ratio with JPMorgan Chase & Co. Both companies are in the financials industries, so we can compare the P/B ratio between the two companies. The comparison helps us to derive the conclusion that JPMorgan Chase & Co is more undervalued by the market compared to Bank of America because it has a lower P/B ratio.