👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 2:53:47 PM
PoW, PoS
What is PoW
Mentioned in Decentralized Finance (De-Fi) and Hash, a decentralized market does not have a centralized market supervisor to avoid malicious or fraud operations. Therefore, certain computer algorithms and logic are set to prevent this situation from happening. Proof of work is one of these algorithms and is widely used in cryptocurrencies as well as other operations on the blockchain.

The blockchain system is an application of the proof of work function. All “blocks” or data will have a certain hash, which is long strings of numbers for proof of work. A certain set of data only generate one specific hash. But tiny changes in the original data will change the entire hash.
Hash is special because it is a one-way function, meaning it is especially difficult to obtain the original data through the hash, except for performing random trials, which require large computing power. Therefore, only if one certain user has more computing power than the majority of the participants in the system, the system can collapse. Users in the blockchain ecosystem need to use their computer power to authorize a new transaction. This use of computer power to solve complex functions is called Proof of Work. These users are called Miners. The Miner who first authorizes a transaction will receive a reward (usually a certain amount of cryptocurrency).
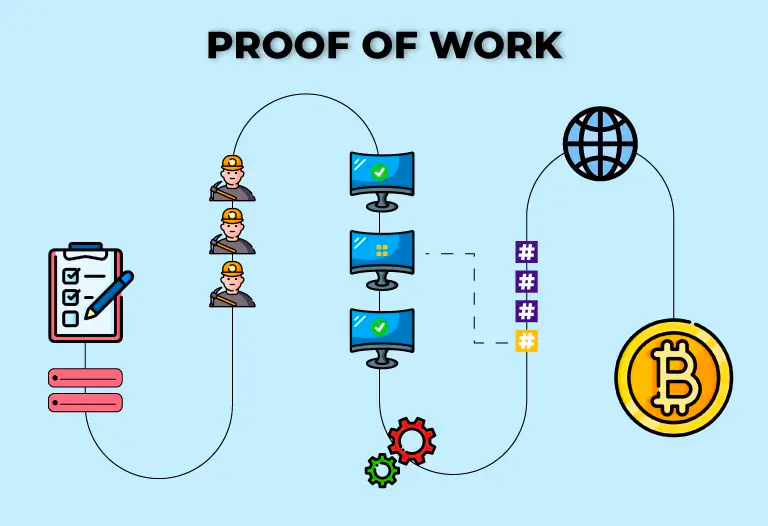
Image source: https://blog.bitnovo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Que-es-Proof-of-Work02.jpg.webp
In fact, in the current major decentralized markets such as the Bitcoin or Ethereum system, there are many active users, which makes fraud operations more difficult. Yet, it is still possible that there are certain defects in the Hash system, which means malicious operations are still possible in theory.
To learn more about the blockchain security system and the possibility of malicious operations, check out the article: 51% Attack.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
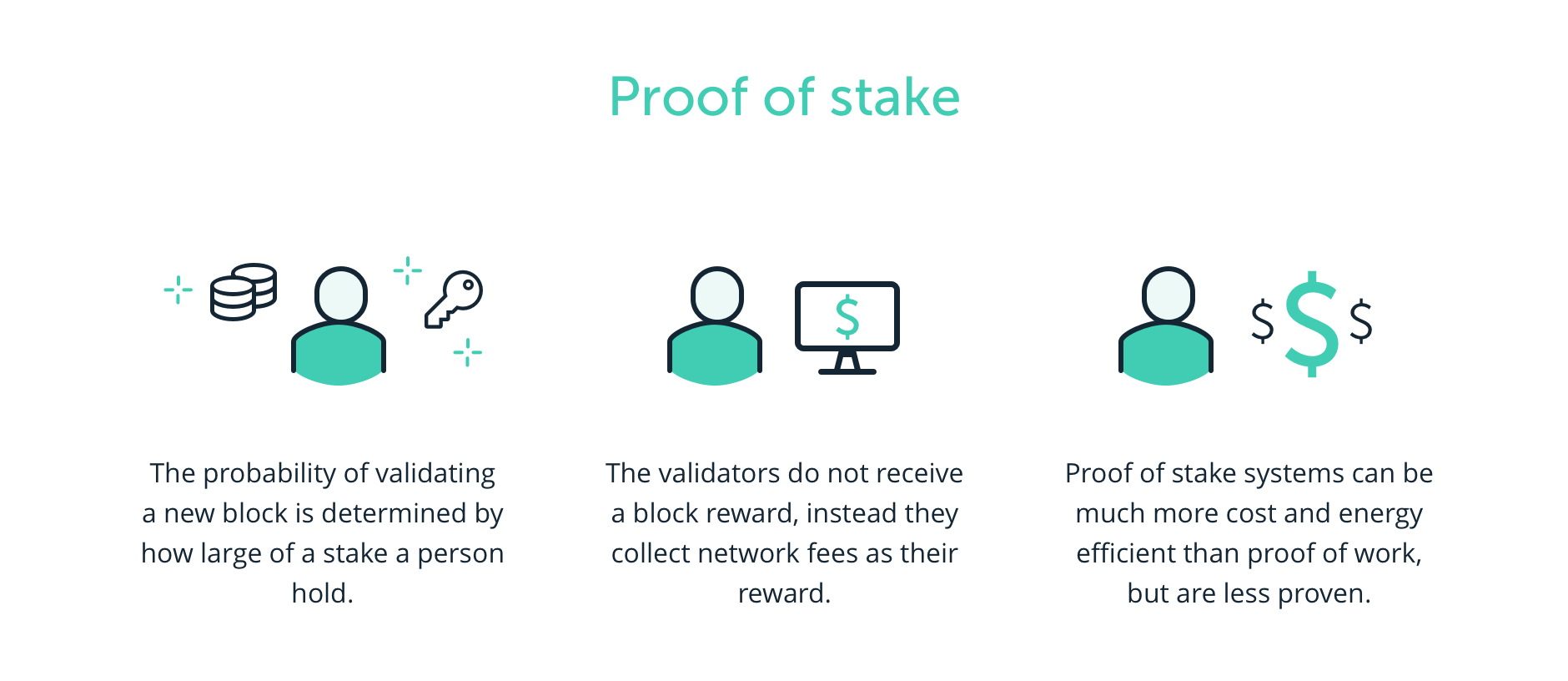
Proof of stake (PoS) is a security feature embedded in the Decentralization market. In a Decentralized Finance (De-Fi) market, there is no centralized market supervisor, therefore Proof of Stake is invented to prevent malicious operations. An alternative to the PoS system is Proof of Work (PoW), which is a more traditional system used by decentralized markets.

Image source: https://publish.one37pm.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/TWITTER-PROMO-70.jpg
In short, PoW uses computer powers to prevent fraud actions. However, in recent years, PoW gained criticism because of its lack of energy efficiency. Carbon footprint, a measurement of the total amount of greenhouse gases, generated during the PoW process is significant. Therefore, PoS is developed to replace PoW as a more optimal system.
As its name implies, proof of stake enables participants to validate new transactions and add them to the blockchain by staking their crypto coins. Therefore, instead of solving complex mathematical equations as PoW requires, the PoS protocol selects a validator node for verifying transactions in a block. If they successfully verified the block and added it to the blockchain, they will receive a network fee as a reward. On the other hand, if they add a block with fraud information, they will lose some of their stakes.
Similar to PoW, there is also a potential risk for a system to apply the PoS protocol. This risk is also called the 51% Attack. For a system that is using a PoS protocol, if one user holds 51% more cryptocurrencies in this system, there will be a possibility for malicious operations. However, since the major cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Bitcoin, or Cardano all have numerous participants, it is practically unlikely for one user to achieve so.