
👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 12:10:46 PM
Efficient Frontier
Pre-Required Knowledge
The Efficient Frontier is a financial theory frequently applied in risk management-related areas. But to understand the concepts and applications of the Efficient Frontier, some previous knowledge of asset’s risk and return is required. It is recommended to read and understand the following concepts before digging into this article:
- Mean, Variance and Covariance
- Standard Deviation and Correlation
- Risk-Return Tradeoff & Volatility
- Risk-Averse, Risk-Neutral, and Risk-Seeking
- Modern Portfolio Theory
- Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)
Although the Efficient Frontier is often viewed as a cornerstone of the Modern Portfolio Theory (and the Efficient Market Hypothesis), understanding these two concepts before reading the Efficient Frontier is beneficial to building a more thorough understanding of risk in finance.
Key Concepts
Harry Markowitz first introduced the concept of an Efficient Frontier in his work Portfolio Selection. He promoted the strategy of using mean-variance optimization to find the most “efficient (AKA optimal) portfolio (asset combination).” In other words, portfolios located on the Efficient Frontier often maximize the risk-adjusted return. Given a certain risk profile, these sets of portfolios on the Efficient Frontier output the highest return rate than any other portfolio combination. Given a certain standard deviation, these sets of portfolios on the Efficient Frontier also give the biggest expected return.

Harry Markowitz. Photo source: https://www.matsonmoney.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Academic-Advisory-Board-Matson-Money-Harry-M-Markowitz-1024x683.jpg
Application: How to Find the Efficient Frontier?
Under most cases, the Efficient Frontier is plotted in an x-y plane, with an x-value marking expected return and a y-value marking risk (standard deviation). Every possible combination of assets (i.e., stocks) can be plotted in this x-y plane, and the combinations on the outer layer are the so-called “Efficient portfolio combinations.” This entire outer layer is defined as the Efficient Frontier.
Therefore, to find the efficient frontier of a selected portfolio, we can simulate all possible combinations (”all combinations” mean a lot of different combinations) and look for the portfolios on the outer layer. To do so, we need first to understand how to calculate the risk and return of an investment portfolio.
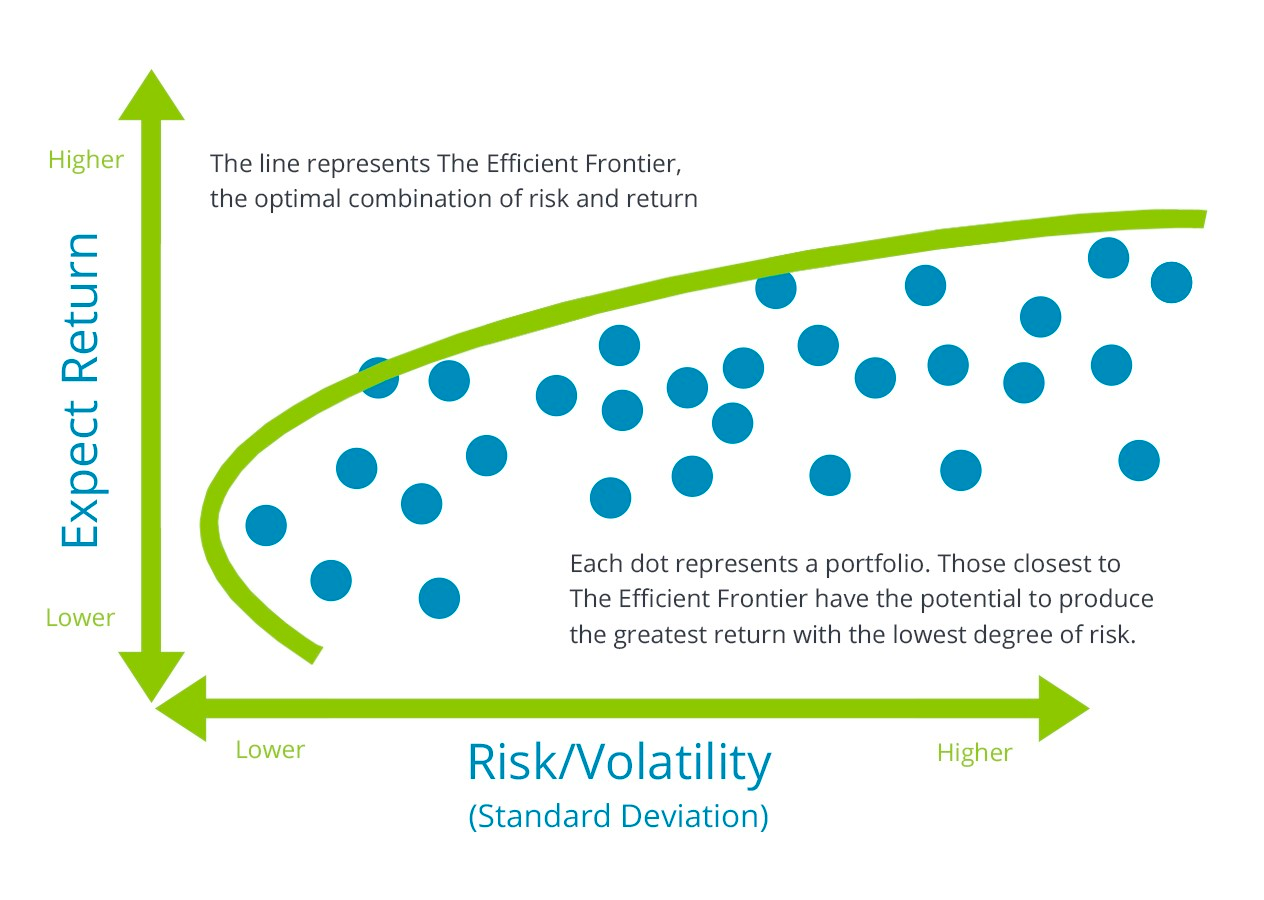
Graph source: https://www.guidedchoice.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/mpt-image-2.jpg\
Return
A detailed explanation for the return of a given portfolio is explained in the article Mean, Variance and Covariance.
An investment portfolio is a collection of financial assets (such as stocks, bonds, ...). Each asset in a portfolio has a different weight, meaning a different amount of money invested. We can derive the expected return of a stock by taking the average of its past returns or implementing the CAPM formula (The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)). Then, after we calculated the expected returns for all assets in a portfolio, we can derive the expected return of this portfolio through the following formula:
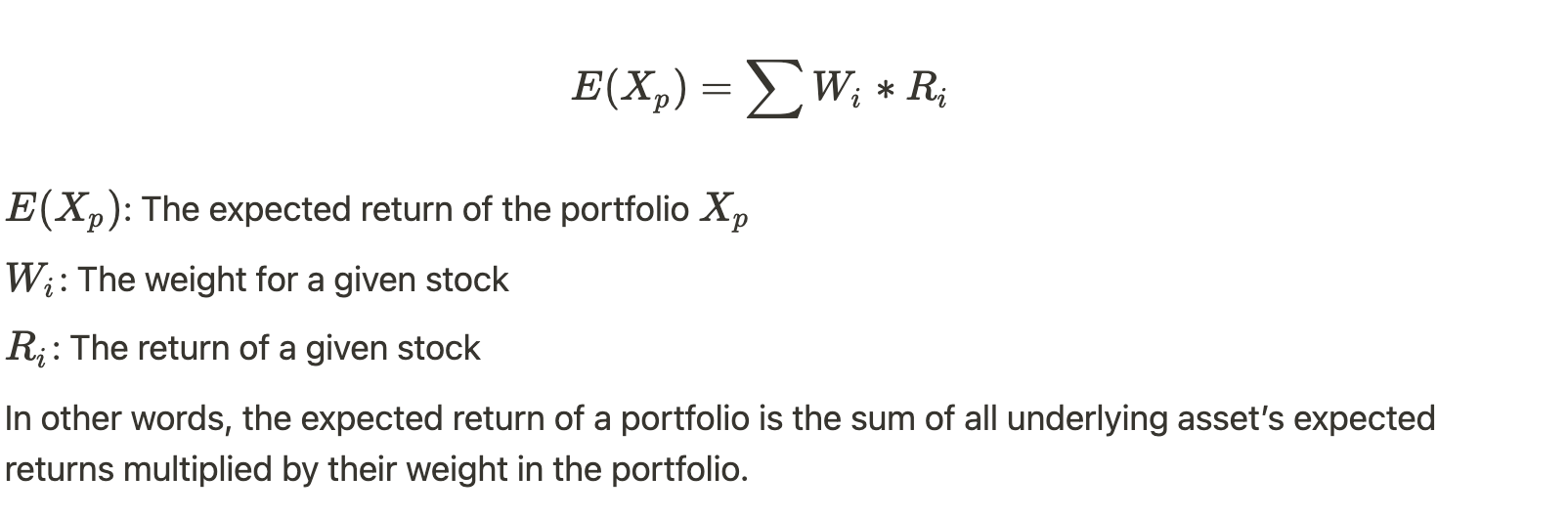
Risk
The risk of a portfolio follows the formula:
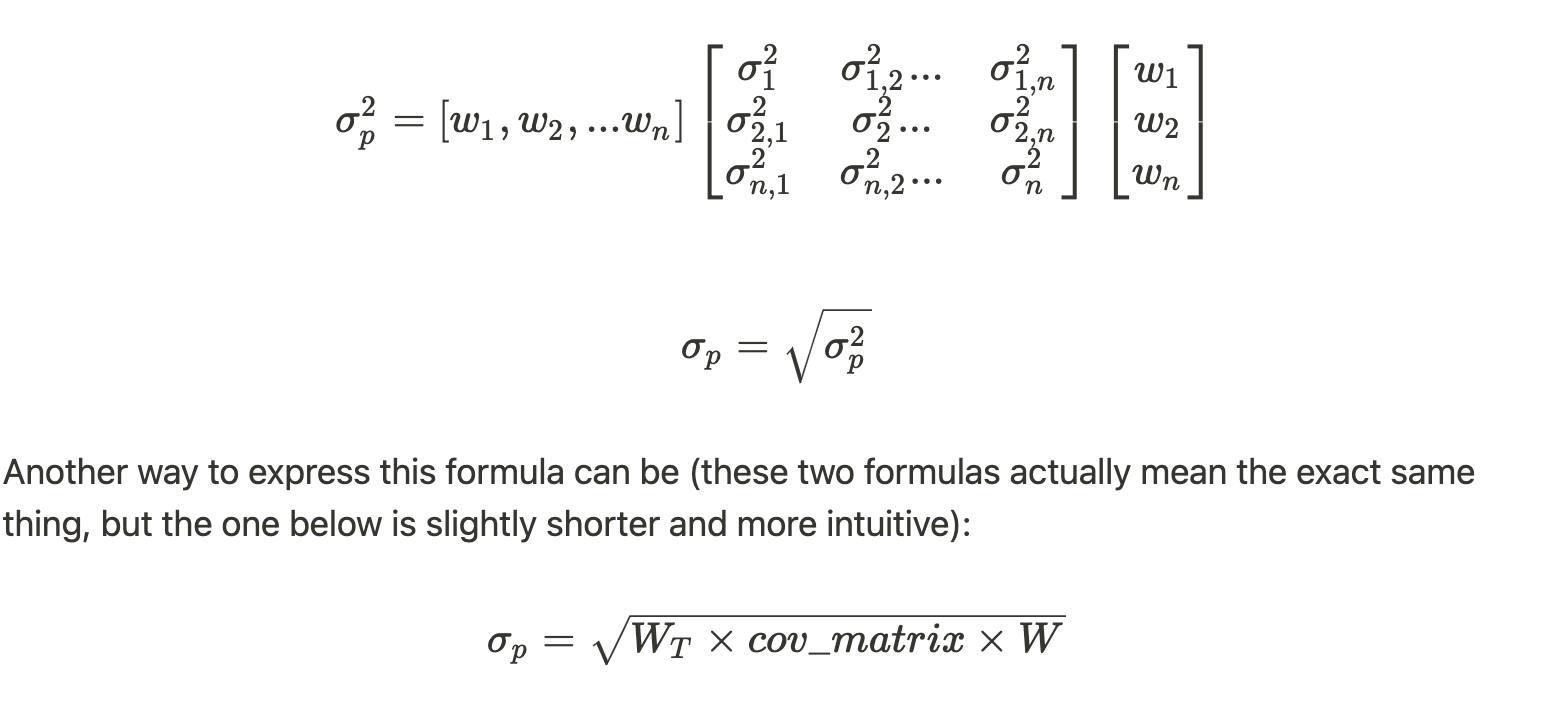
Where:
W_T: The transposed weight in a portfolio
cov_matrix: The variance-covariance matrix. Check out more in the article Mean, Variance and Covariance.
W: The weight in a portfolio.
Plotting
After understanding the calculations for risk and return, we can then derive an x-y coordinate for all potential portfolio combinations. By repeating the calculation process for combinations with different weights for sufficient amount of times (i.e., 10,000 times), we can derive the following graph:
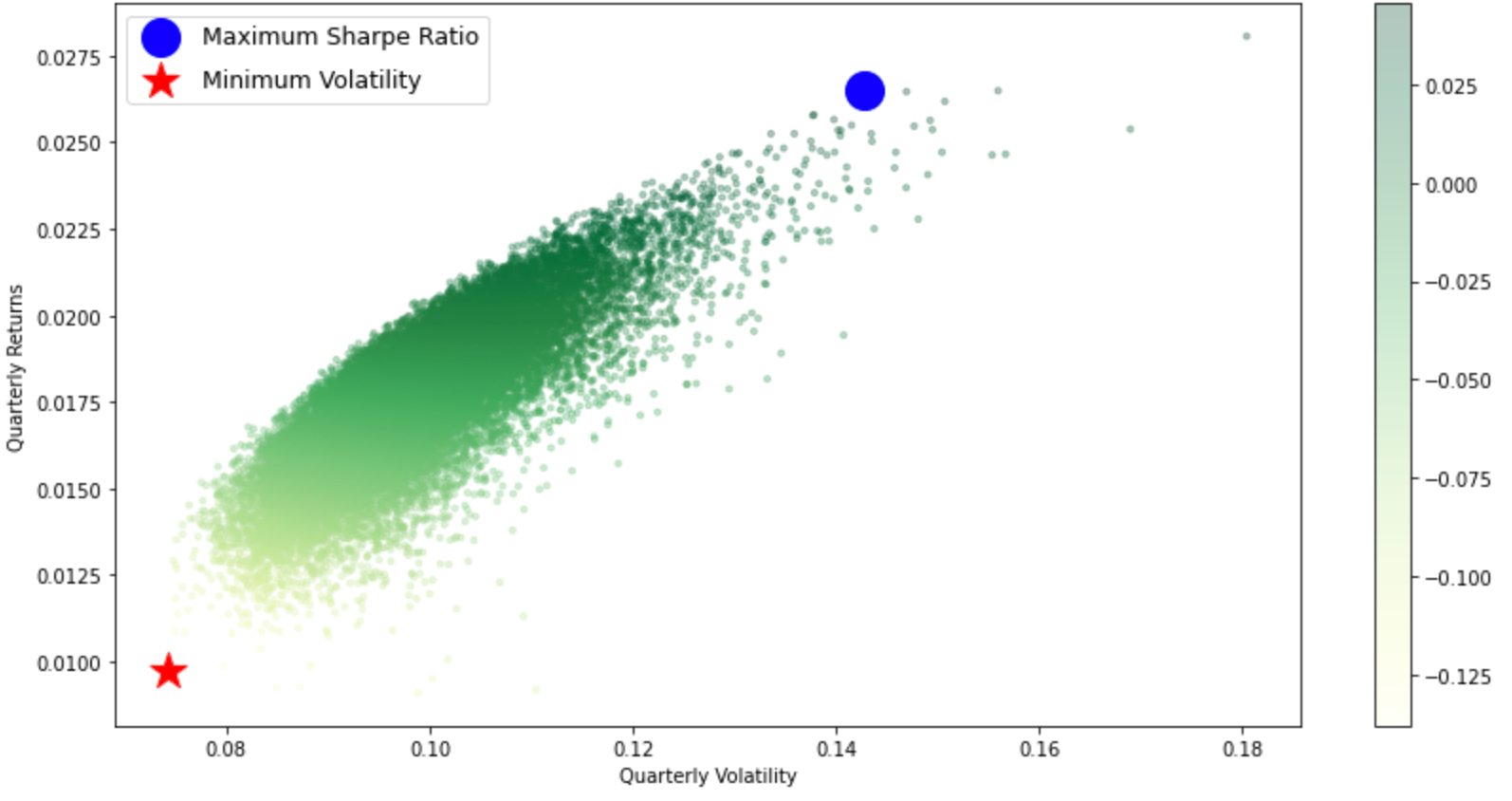
The outer layer will then be the Efficient Frontier for this portfolio:
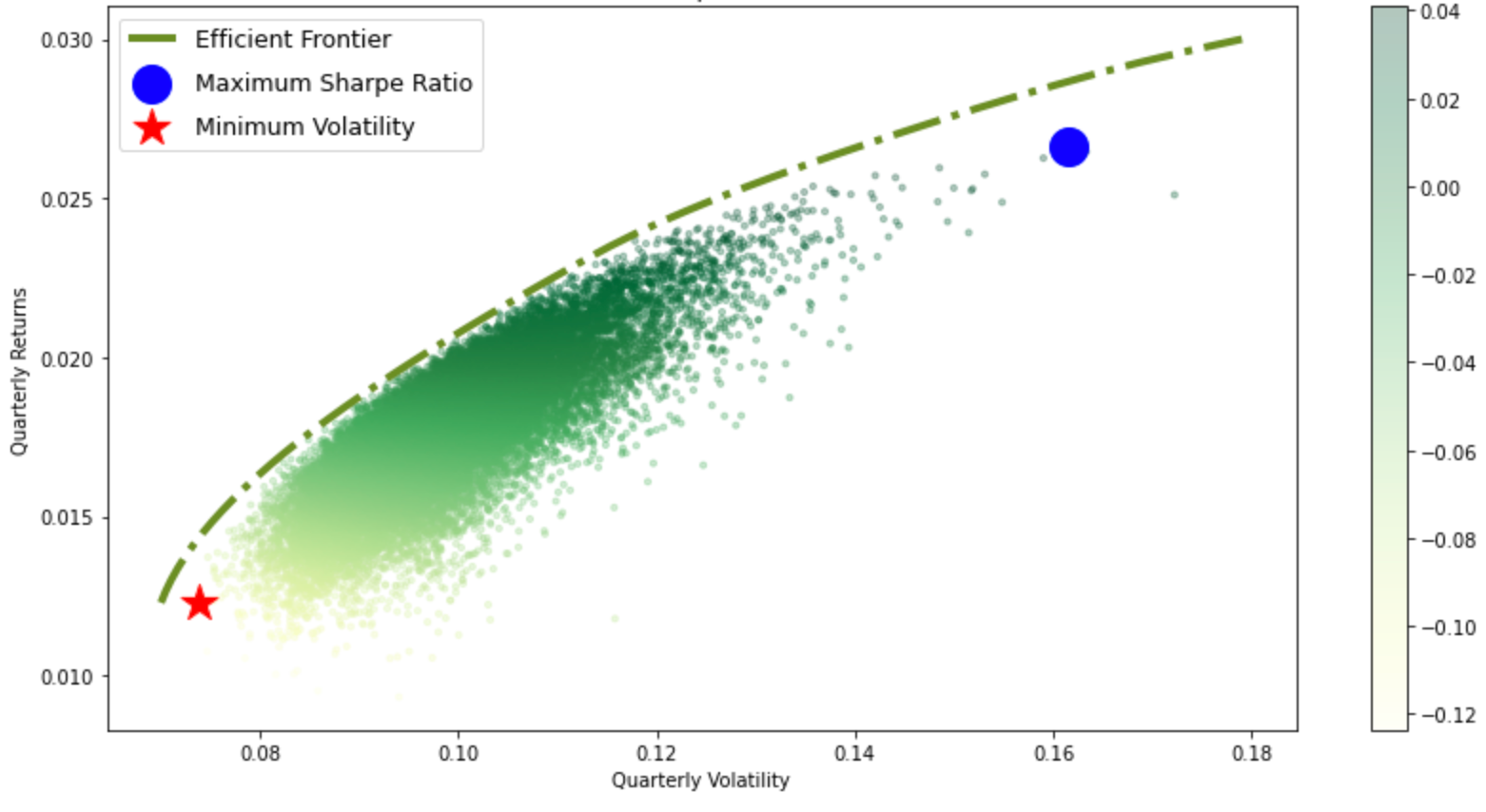
Further explanation on the application of efficient frontier and how to find the combination can be found in the article: Portfolio Management: Using Python.