
👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 3:25:00 PM
Decentralized Derivatives
Ce-Fi vs De-Fi
Starting in 2020, the concept of De-Fi encountered a new peak. At the same time, people started to discuss the differences between centralized finance and decentralized finance. Debates were held for supporters of both sides to argue.
To have a glimpse of the mechanism behind two systems, imagine two scenarios:
Scenario One, Centralized Finance:
You earned a $1000 prize from the lottery. You hope to save this money and make some profit out of it. In a centralized financial system, you can choose to save money in a bank. Your money will be guarded by the workers in the bank and you will earn a certain amount of interest rate each year. You also need to pay a proportion of your money to the bank as a reward for them guarding your money.
Scenario Two, De-Fi:
You have an alternative choice. You can choose to save this money in a decentralized system. In this system, you will have a wallet and a ledger on the blockchain to track your transactions. In this system, there is no guard or workers securing your money. Instead, cryptography and Hash systems are programmed to keep your money safe. You also need to pay a certain amount of fee, called the Gas fee, as a reward to users who help authenticate your transaction.
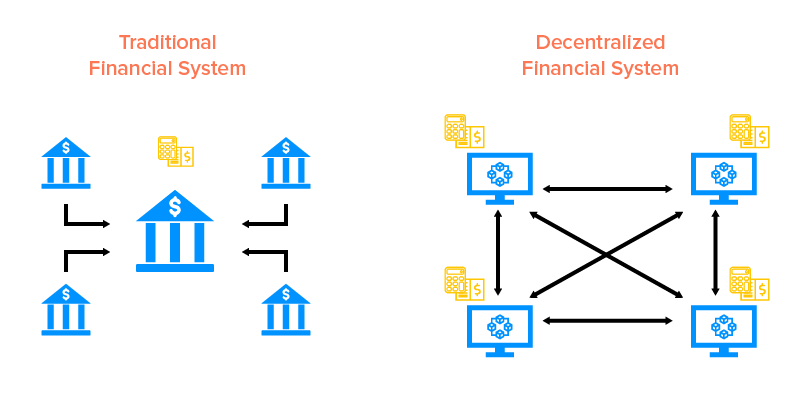
Now you see the difference between centralized finance and De-Fi. In the finance world, there are often more complex applications in both systems. An example is financial derivatives.
- In short, a derivative is a form of financial contract between parties that derive its value from an underlying asset. Some common examples are stocks, bonds, options, currencies, futures, and commodities.
In Part I: Applications of Defi - Cryptocurrency, a detailed explanation of currency is provided. In this article, further analysis of some other derivatives will be demonstrated.
1. Futures
Futures, as its name “future” indicates, are derivatives that have a contract agreement to make transactions (buy or sell) of a commodity at a predetermined date and price.
Futures work very straightforwardly in Ce-Fi. A specific maturity date (date for the transaction) and expiration (price) are set previously. In De-Fi, a new type of futures, called Perpetual Futures (AKA Perps), are developed.
Perps differ from the centralized applications of futures because there is no expiry date. People can hold Perps as long as they like. Other than that, Perps resemble the characteristics of other futures. It is based on an underlying commodity or index price. Some De-Fi-based Perps are developed, including Defi-Perp, which tracks the price of a range of cryptocurrencies. Perps are most commonly traded on Decentralized Exchanges such as Binance, but some are also available on centralized exchanges.
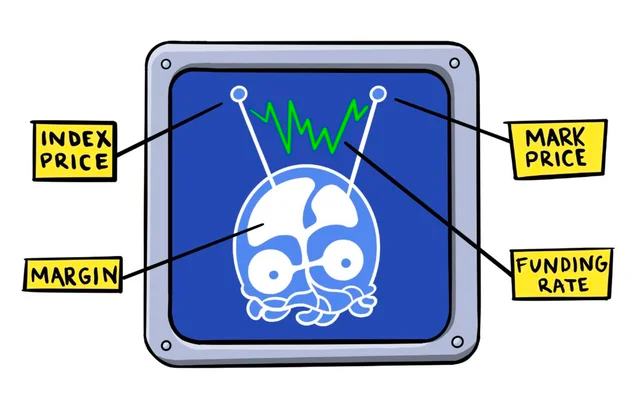
2. Options
Another type of financial derivative that exists in both centralized and decentralized finance systems is options. Options are derivatives that give investors the right to trade the future value of a market. The main difference between options and futures is that options give investors the right but not the obligation to trade a certain asset at a certain price given a certain date.
Similar to futures, there is also an expiration date for options. After this date, the investor will no longer have the right to buy or sell at the predetermined price, which means the option will become worthless.
As cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin started to gain attention, crypto-related options surged in popularity. Yet, the majority of the trading volume for these options centered on centralized cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Deribit, Okx, and FTX.
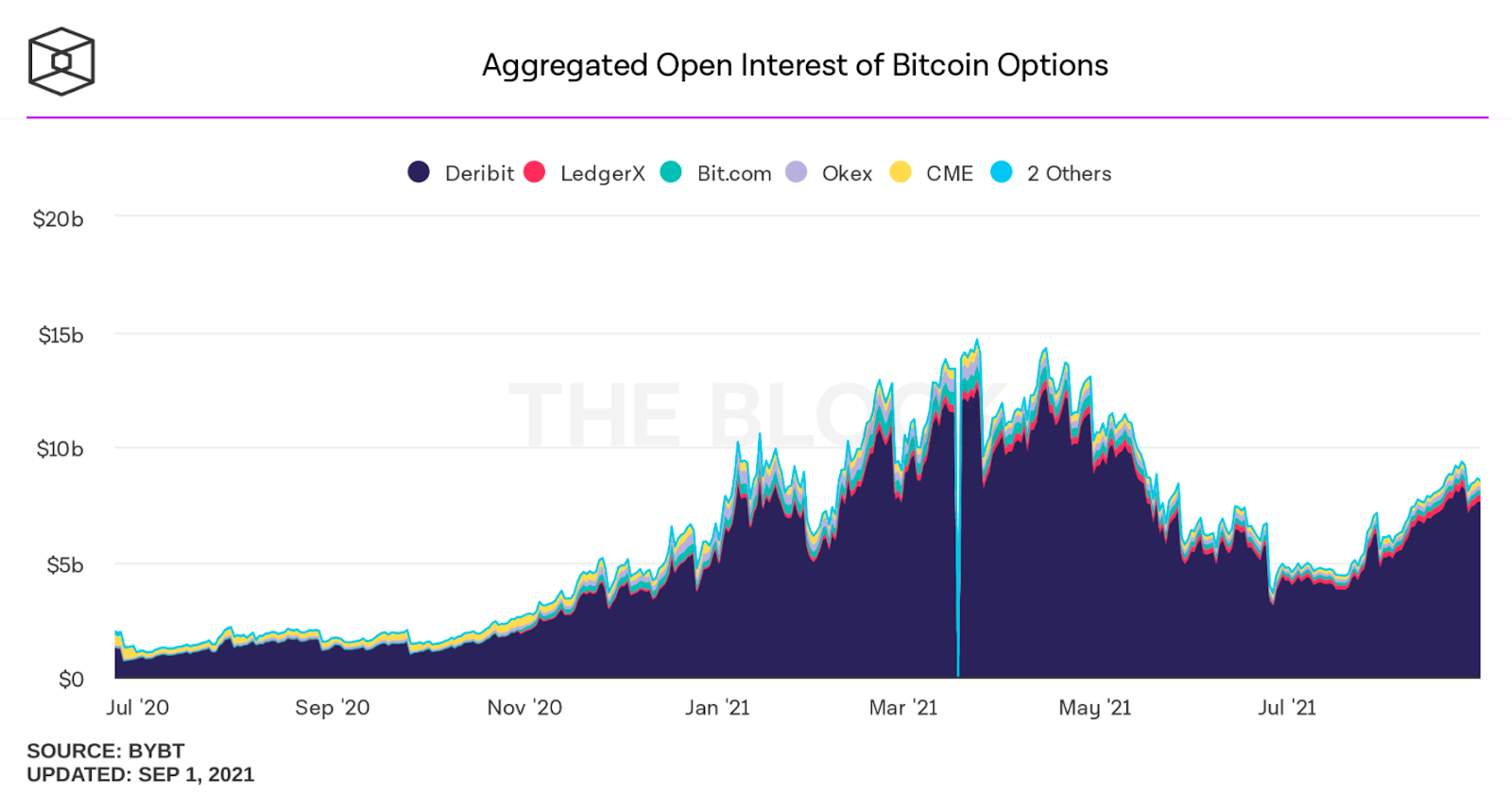
Image source: https://blog.lyra.finance/crypto-options-vs-perps/
On the other hand, unlike Perps, options have not yet gained much interest for their on-chain applications. Most trades are gathered in the centralized cryptocurrency exchanges mentioned above. This can be explained by the low liquidity and high-risk nature of options.