
👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 8:41:52 AM
DCF: Using Excel
Pre-Required Concepts
This article will provide a practical explanation of the application of the DCF model using Excel. The sample company chosen in this article is PayPal. It is highly recommended to read through the fundamental valuation and accounting sections before reading this article.
Discounted Cash Flow Model: What is It About?
The discounted cash flow model is a financial valuation model that is based on the Time Value of Money (TVM). This valuation model aims to derive the value of an investment today (AKA the intrinsic value of an investment) by forecasting the sum of money this investment can generate in the future. The DCF model can be applied in many different areas, such as a company, security, or project investment.
Here a DCF model will be applied to a company’s stock. The stock’s intrinsic price, according to DCF, is equal to all of the underlying company’s future Free Cash Flow discounted at Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). In this case, WACC is equivalent to the discount rate since it measures the cost for the companies to get funds (through equity and debt), which is also the minimum expected free cash flow return the company has to generate in order to sustain the business.
Therefore, the DCF model can be summarized through this formula:
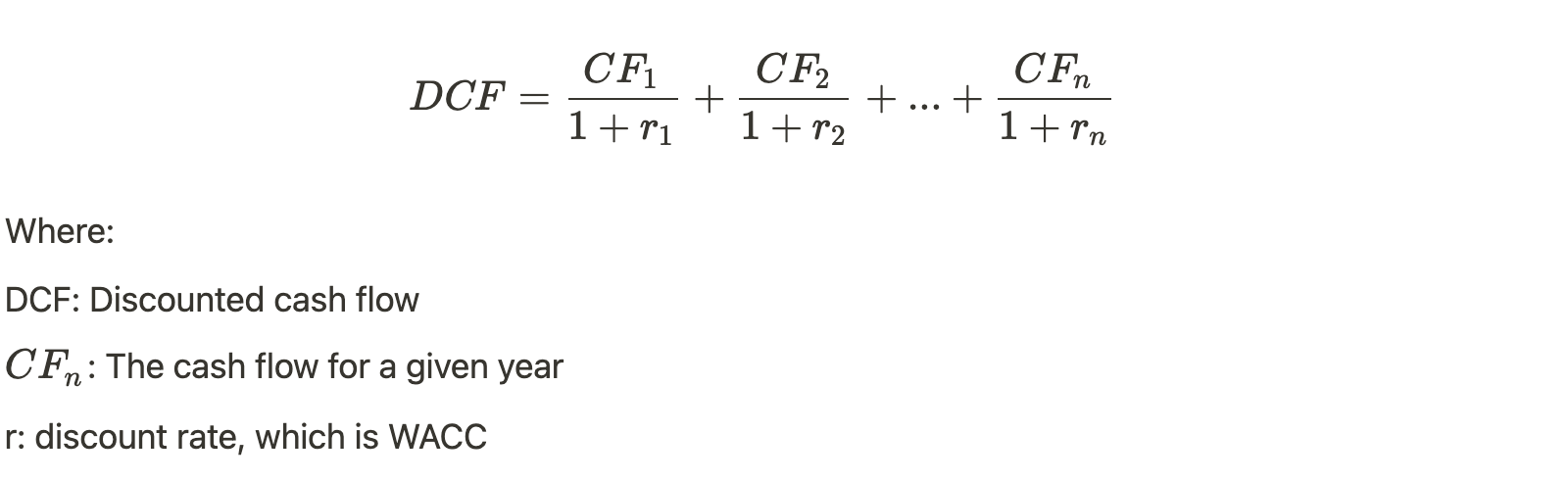
Step One: Forecast on Financial Statements
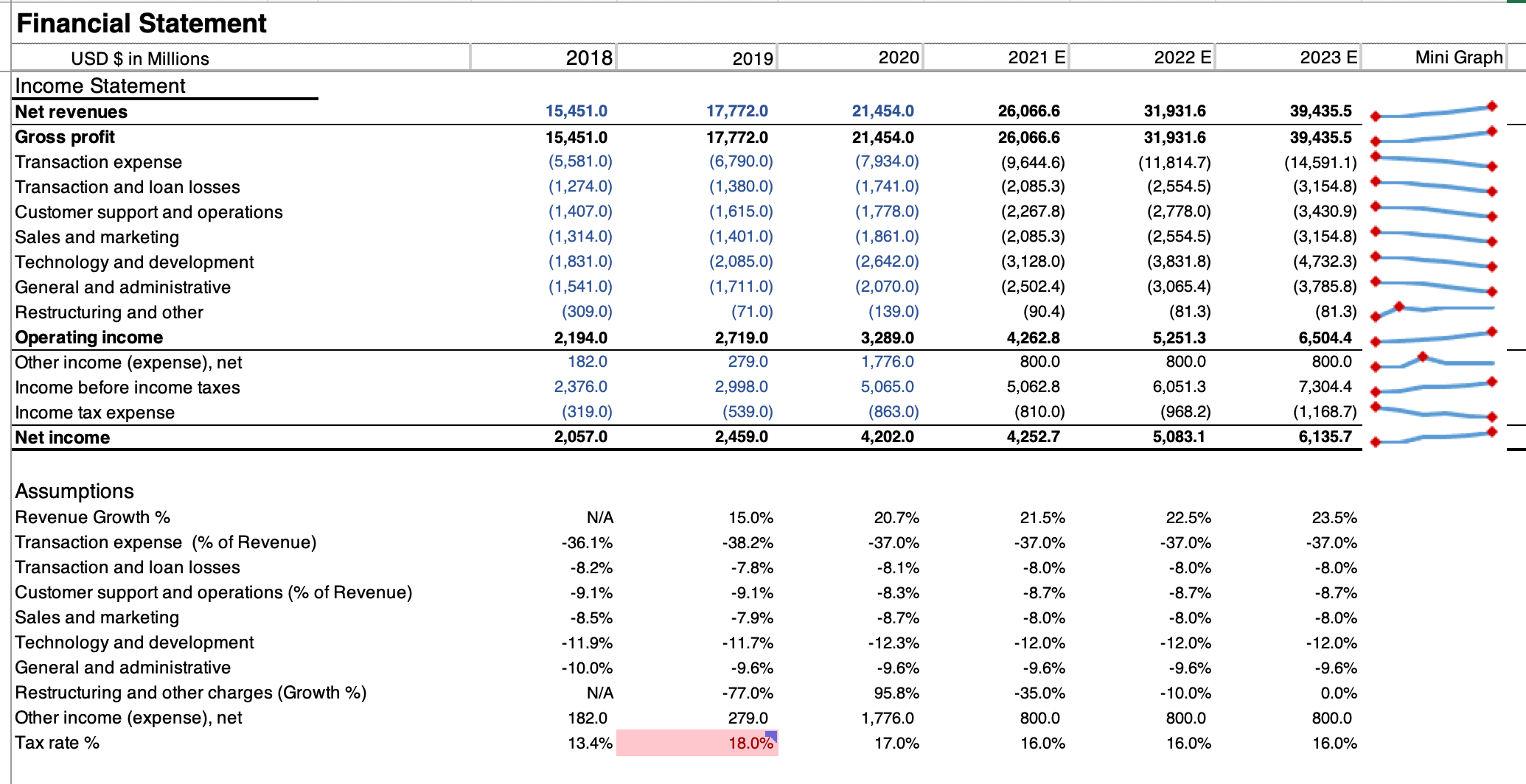
The first step of the DCF model is to analyze the three financial statements. A detailed explanation can be found in Excel: Income Statement Analysis, Excel: Balance Sheet Analysis, and Excel: Balance Sheet Analysis. After breaking down the three financial statements, the next step is to perform forecasts on the three statements. Yet it is important to remember that to make appropriate forecasts, information is crucial. Therefore, an essential step before performing the actual forecasts is to “know the company”: collect news, understand the major products of the company, learn about the management team, etc. This ensures us make more reasonable and accurate assumptions.
Some recommended websites to collect information are:
Some recommended websites to collect information are:
- Simply Wall St for company overview: Simply Wall St - Stock & Sector Analysis Made Simple
- Finviz to see professional analyst’s opinions: FINVIZ.com - Stock Screener
- Wall Street Journal to learn the most recent news: The Wall Street Journal - Breaking News, Business, Financial & Economic News, World News and Video
Here is an example of the forecast for PayPal’s income statement. The balance sheet and cash flow statement follow the same logic:
Step One: Financial Forecast
Financial Statement Forecast Flow Chart
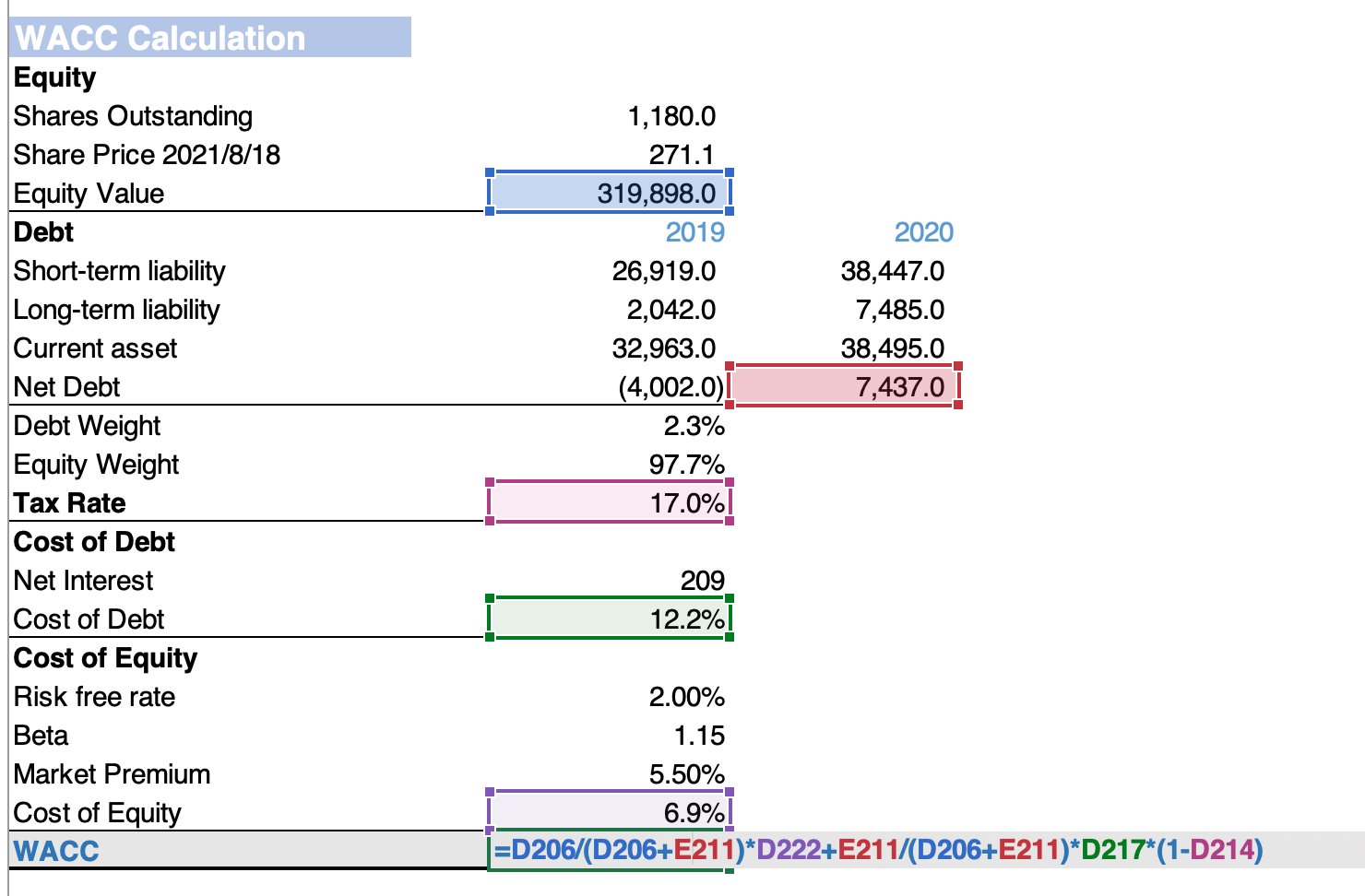
Step Two: WACC Calculation
The second step of the DCF model is to derive the discount rate or WACC. The article Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) provides a detailed explanation of how to derive each of the components inside WACC.
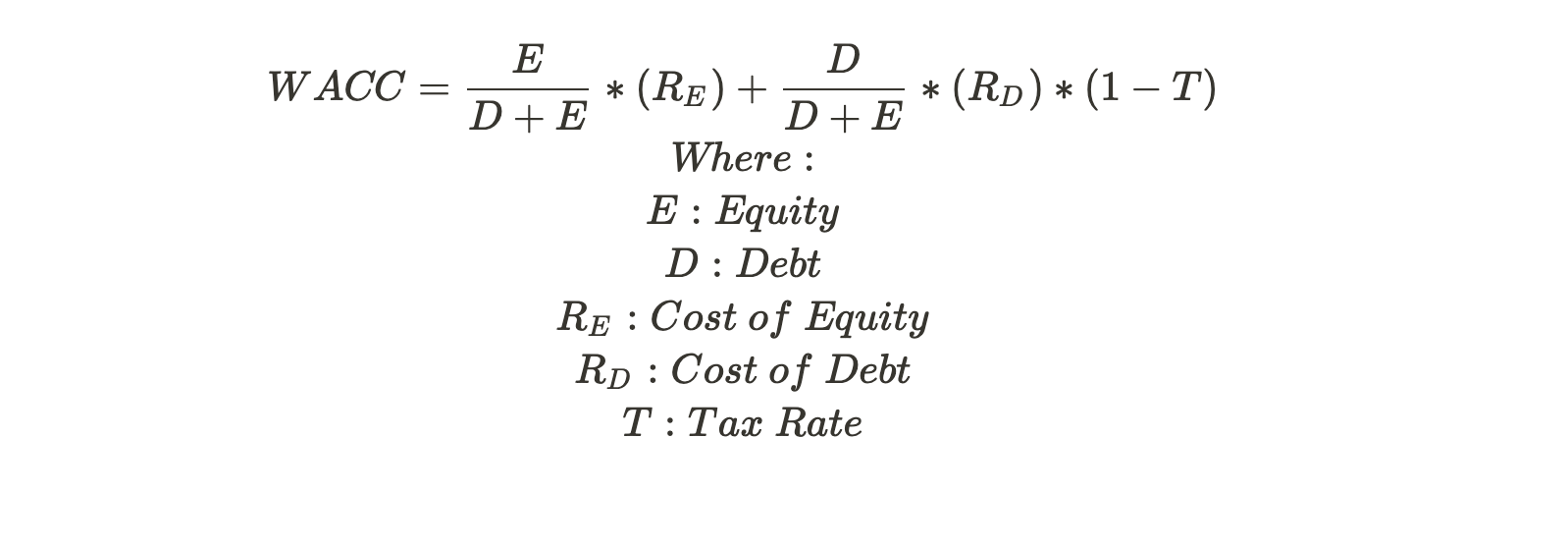
For PayPal’s case, we chose to use the CAPM formula to derive the cost of equity since PayPal is a typical growth stock and does not offer a dividend (which makes Gordon’s Model ineffective).
Step Three: Discounted Cash Flow Model Performance
After all the preparation steps, we come to the final step to discount the cash flow. Under this step, we have several small procedures to complete.
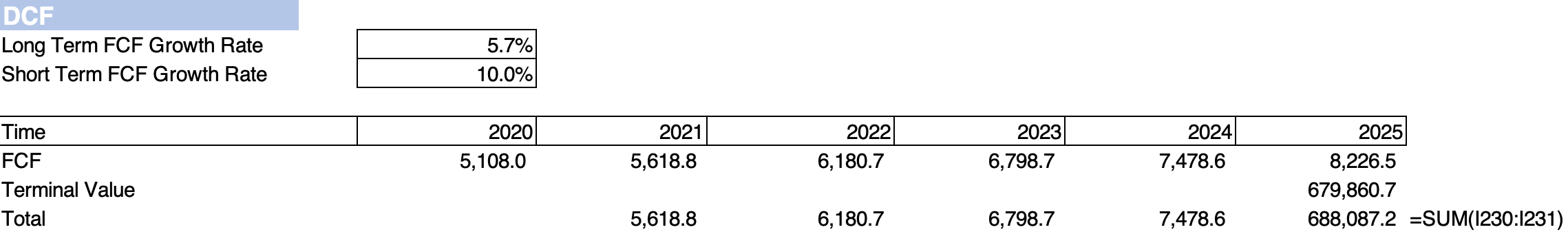
A. Future Free Cash Flow
The formula for free cash flow can be found in Free Cash Flow(FCF). To derive the future free cash flow, we need a long-term and a short-term FCF growth rate. We can derive this growth rate according to the financial forecasts we did in Step One.
In this case, we consider FCF within the future five years as “short-term.” The short term FCF is calculated through the formula:
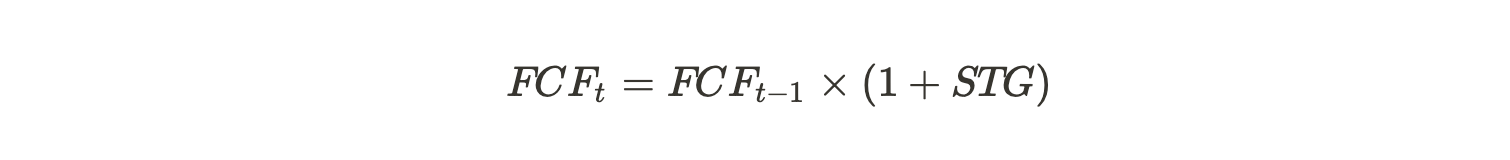
STG: Short-term growth rate
The sum of all FCF after the fifth year is considered the long-term FCF, which is also called the “terminal value.” It follows the formula:
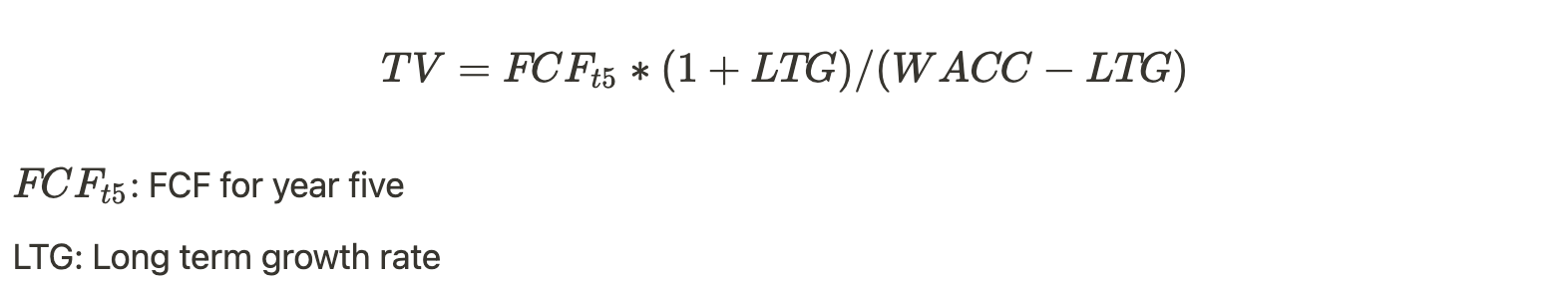
B. Discount Future FCF
According to the Time Value of Money (TVM), the intrinsic enterprise value is believed to be the discounted sum of future FCF discounted at WACC. In Excel, the handy formula NPV(discount rate, value1, value2, … value n) conveniently calculates the discounted intrinsic value.
After deriving the intrinsic enterprise value, we can add the cash and subtract the debt to calculate the equity value. If we divide the equity value by the total shares outstanding, we will get the intrinsic stock price. This means we can compare the intrinsic stock price and the actual current stock price to check whether the current price is overvalued or undervalued.
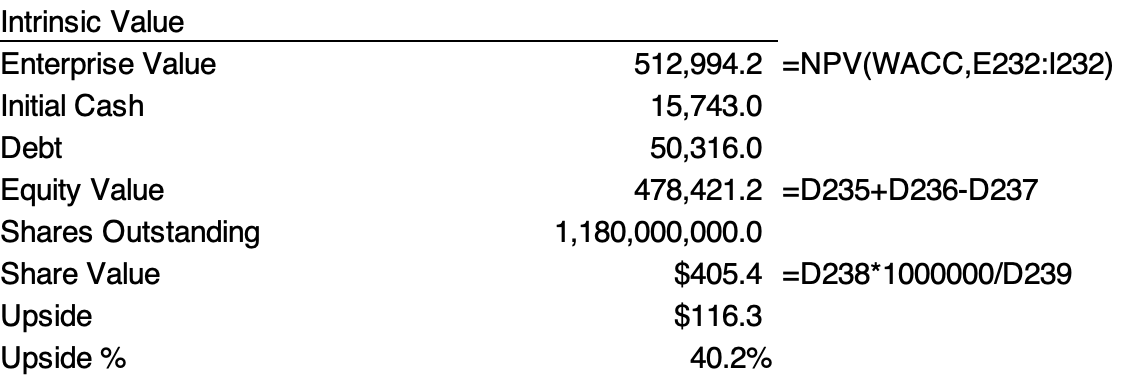
In this case, we are quite optimistic about PayPal’s price and believe there is a 40.2% growth space for the future stock price.
Note: All the calculations and analyses based on PayPal in this article are based on pure assumptions for future stock growth. Therefore, this article does not recommend any stock, and the analysis can only be used for educational purposes.