
👾 Game Master
6/21/2022, 3:00:24 PM
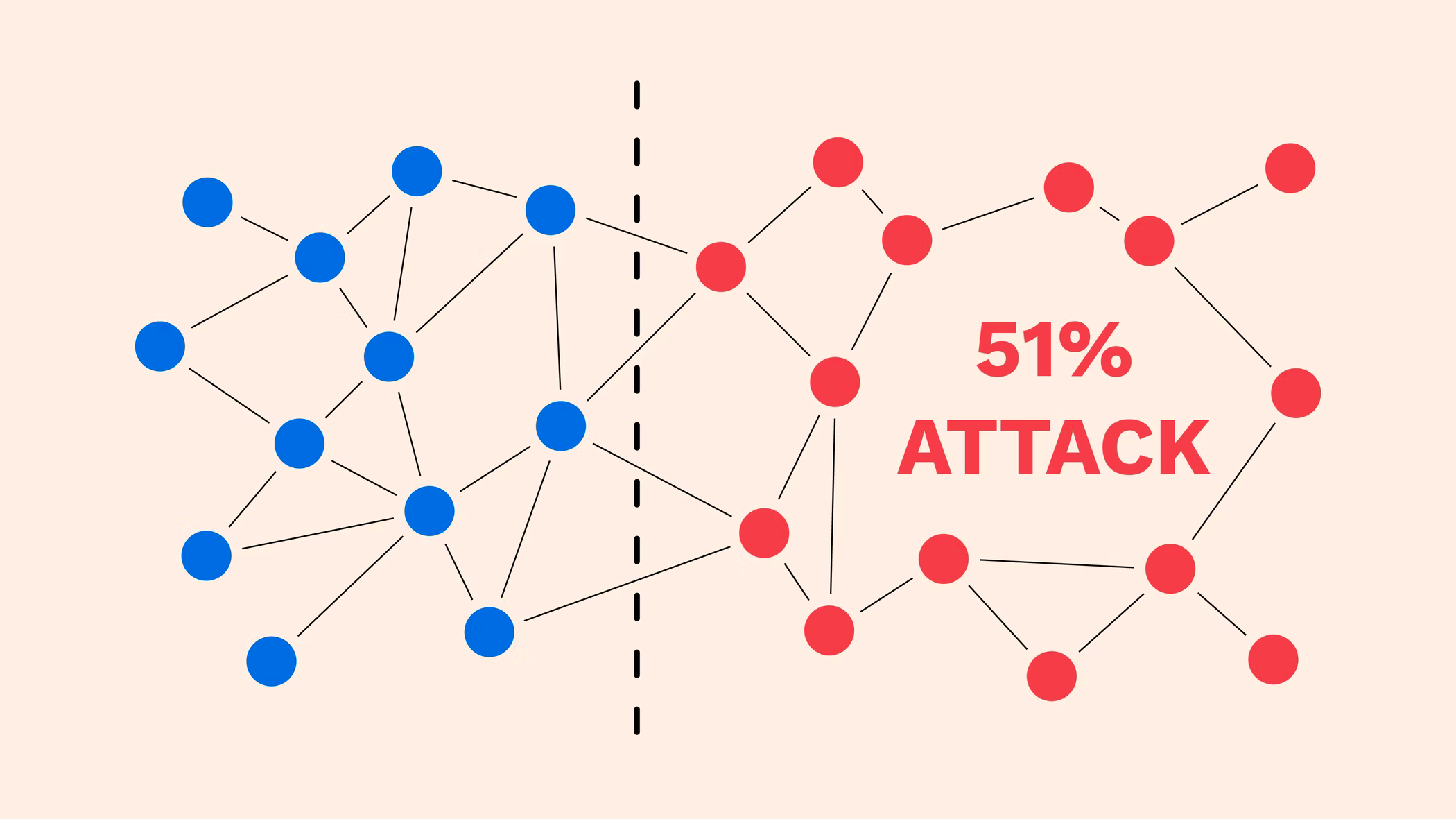
51% Attack
What is the 51% Attack?
When people think about blockchain as a technology, two adjectives usually pop up in their minds: trustworthy and secure. Blockchain stands out from the other security systems because it is a technology that is based on Decentralization. This means that no human is supervising the system. Instead, the entire technology relies on Hash. While blockchain is often considered a secure system, there is a potential risk of security meltdown. This theoretical risk (the word theoretical means that it is currently less possible for this to occur but uncertain in the future) is called the 51% attack.
Hash & Principle Behind 51% Attack
The entire blockchain relies highly on the so-called hash. A hash results from an encrypted chain of letters and numbers. It is a mathematical code that can translate input into a sophisticated output. The hash is always "one-way-around,” which means that it is not reversible. Hash is an important part of the blockchain and cryptocurrency. Hash makes the blockchain a secure system because the only solution to derive the original input through the output is by doing random tests. However, this process takes a HUGE computational power and thus makes malicious operations (currently) impossible to achieve.
A 51% attack happens when one participant controls over 51% of the environment’s mining or validation power (i.e., more computational powers than most participants in the system). This participant can then use the privilege to create invalid transactions, destroy legitimate transactions, and other malicious operations for financial gain.
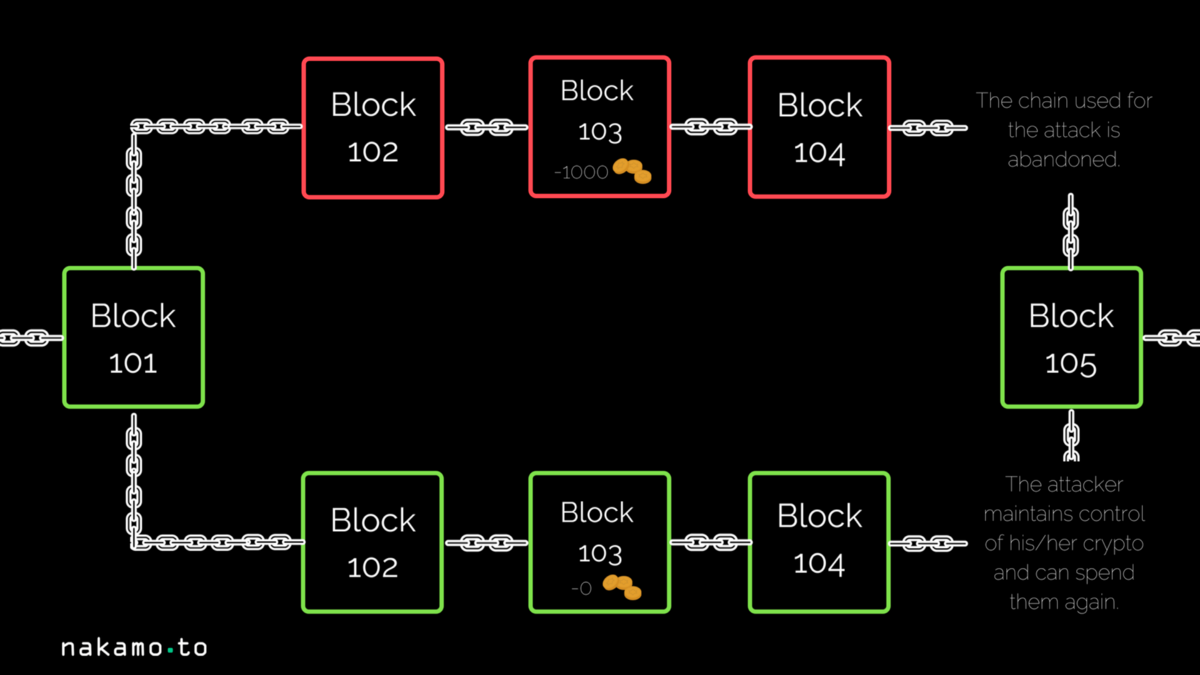
Image source: https://miro.medium.com/max/1200/1*L-2SBU7WHQTbwgnDQr72Tw.png
Good News!
Fortunately, the 51% attack on major blockchain networks such as Bitcoin or Ethereum is relatively unlikely. Since there are many participants in the system, it is nearly impossible for one user to have more computational power than half of the system. However, if any shortcuts in reversing the hash are found in the future, the blockchain will collapse, and security will evaporate.